The suspension system of a car is much more than just a set of springs and shock absorbers. It is a crucial component that plays a significant role in enhancing your car’s ride comfort, handling, and overall safety. Understanding the science behind suspension systems can help you make informed decisions about maintaining, upgrading, or replacing your car’s suspension setup. Here, we delve into the fascinating world of automotive suspension technology.
What is Suspension?
In simple terms, a car’s suspension system is a network of components that connect the vehicle’s body to the wheels. Its primary purpose is to ensure that the wheels maintain contact with the road surface, providing optimal traction and stability while absorbing various road imperfections such as bumps, potholes, and vibrations.
Components of Suspension Systems
A typical suspension system consists of several key components:
Springs: Provide support and absorb shocks.
Shock absorbers (dampers): Control the motion of springs, preventing excessive bouncing and vibrations.
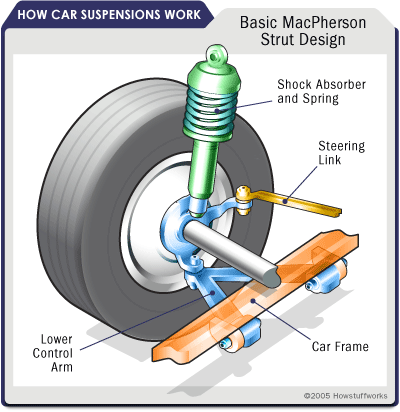
Struts: Integrated coil spring and shock absorber units that simplify the suspension design.
Control arms: Link the wheels to the frame, allowing up and down movement while maintaining stability.
Stabilizer bars: Minimize body roll during cornering by connecting the suspension components across the vehicle’s width.
Bushings: Provide flexibility and quiet operation by reducing friction between moving parts.
Types of Suspension Systems
There are several types of suspension systems found in modern cars:
1. Independent Suspension
Independent suspension allows each wheel to move independently, ensuring better traction, improved ride comfort, and enhanced handling. It is further classified into:
MacPherson strut suspension
Double wishbone suspension
Multi-link suspension
2. Dependent Suspension
Dependent suspension, also known as solid axle suspension, connects the wheels on one axle together. While it may be less costly, it generally delivers a rougher ride and reduces overall handling performance compared to independent suspension.
The Science Behind Suspension Systems
Proper suspension design requires a delicate balance between various factors, including spring rates, damping characteristics, and body motions.
1. Springs
Springs are responsible for supporting the vehicle’s weight and absorbing shocks from road irregularities. They come in various types, including coil springs, leaf springs, and air springs. The spring rate determines how stiff or soft the suspension feels, impacting both ride comfort and handling. A softer spring offers a smoother ride but sacrifices handling precision, while a stiffer spring improves handling but compromises ride comfort.
2. Shock Absorbers
Shock absorbers, or dampers, work in conjunction with springs to control the movement of the suspension. They absorb energy from the springs’ compression and extension cycles, ensuring the tire stays in contact with the road. By damping the spring’s oscillations, shock absorbers prevent excessive bouncing, maintaining stability and providing a more controlled ride.
3. Anti-roll Bars
Anti-roll bars, also known as stabilizer bars, play a crucial role in controlling body roll during cornering. By connecting the left and right suspension components, they distribute the force more evenly, reducing the lateral load transfer and improving stability through turns.
4. Bushings
Bushings, made from rubber or polyurethane, reduce friction and isolate vibrations between various suspension components. They allow controlled movement while minimizing noise and improving ride quality.
Suspension Tuning and Upgrades
Car enthusiasts often seek to improve their car’s suspension for enhanced performance and personalized driving experiences.
1. Adjustable Suspension
Many high-performance vehicles come equipped with adjustable suspension systems that allow drivers to fine-tune the suspension’s characteristics to match their preferences. Adjustable coilovers and electronic dampers offer flexibility in adjusting the ride height, damping rates, and overall stiffness.
2. Upgraded Springs and Shocks
Replacing the factory springs and shock absorbers with performance-oriented aftermarket options can significantly enhance a car’s handling capabilities. These upgrades offer improved control, reduced body roll, and better responsiveness for more spirited driving experiences.
3. Polyurethane Bushings
Replacing stock rubber bushings with polyurethane alternatives can deliver sharper and more precise suspension response. Polyurethane bushings exhibit less deflection, allowing for better energy transfer and increased suspension efficiency.
Conclusion
Understanding the science behind suspension systems is vital for car enthusiasts and everyday drivers alike. A well-designed and properly maintained suspension setup can vastly improve a car’s ride comfort, handling, and overall performance. Whether you choose to stick with the stock setup or explore upgrade options, ensuring your suspension system is in optimal condition will result in a safer and more enjoyable driving experience.

